Estimated reading time: 4 mins
Inflammation is one of the body’s natural responses to injury and infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to a wide range of health issues. Inflammation is a natural response of the body to any type of injury or infection, and it’s essential for aiding in healing and fighting off disease. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to serious health problems.
Chronic inflammation is linked to a variety of diseases, including heart disease, cancer, diabetes, obesity and Alzheimer’s. When your body experiences inflammation, it triggers an immune response which causes white blood cells to release chemicals called cytokines. These cytokines help fight off whatever is causing the inflammation and aid in healing the area. However, when this process becomes prolonged due to chronic inflammation, these cytokines can start to damage healthy cells as well as target tissues surrounding the area of inflammation. This damage leads to issues like tissue breakdown and damage to organs over time. Chronic inflammation increases your risk for certain diseases because your body is constantly trying to fight something that isn’t actually present. This puts extra strain on your immune system which can eventually lead to illness or disease if not addressed properly.
While the cause of inflammation can vary from person to person, there are some common triggers that you should be aware of. In this article, I will explore the top ten causes of inflammation and provide examples for each.
1. Injury

One of the most common causes of inflammation is an injury. Whether you twist your ankle or cut yourself while cooking dinner, any type of physical trauma can trigger your body’s inflammatory response. Swelling, redness and pain are all signs that your body is trying to repair itself by sending cells to the affected area.
2. Infection
Bacteria, viruses and fungi can all take hold in our bodies and cause us discomfort as well as inflammation. When we get sick with a cold or flu virus, our bodies respond by producing cytokines which act as a call-to-arms for white blood cells to come fight off the infection. This influx of cells leads to swelling in the affected area which is often accompanied by fever and chills.
3. Allergies
Allergens such as dust mites, pollen or pet dander can cause our immune systems to overreact resulting in an allergic reaction which usually involves redness and swelling in various parts of our bodies. Symptoms may include itching eyes, runny nose or even hives on skin depending on how severe the reaction is.
4. Stress


Chronic stress has been linked with increased levels of inflammatory markers which could contribute towards a range of health issues including depression and heart disease. Stress hormones like cortisol suppress our immune system making us more susceptible to infections which then further increase inflammation levels in our bodies.
5. Poor diet
Eating too much sugary or processed food along with not getting enough vitamins and minerals has been shown to contribute towards higher levels of inflammation in both adults and children alike. Not only do these types of foods lack essential nutrients but they also contain trans fats which have been linked with increased risk for developing diseases, such as diabetes or heart disease, due to their pro-inflammatory effects on the body’s cells. Same goes for eating too much seed oil packed full of Omega-6 fatty acids.
6. Smoking
Smoking has long been considered bad for our health but recent research suggests that its damaging effects go beyond just heart disease; studies have found that smokers have higher levels of inflammatory biomarkers than non-smokers suggesting that smoking could be contributing towards systemic inflammation in their bodies over time if left unchecked.
7. Alcohol consumption


Excessive drinking has been linked with increased risk for developing certain types cancer due its impact on inflammation levels within our bodies; alcohol damages epithelial tissue which line out organs leading them become inflamed making them more vulnerable attacks from pathogens like bacteria or viruses .
8. Ageing
As we age it becomes increasingly difficult for us maintain healthy levels of inflammatory cytokines as well keeping other vital hormones in balance; this means even small injuries can result in greater amounts swelling than they would in younger individuals, who still retain full functionality of their immune systems.
9. Air pollution
Inhaling smoke whether it be second hand tobacco smoke or a burning wood stove can increase the amount of particles entering into your lungs, leading to irritation of bronchial tubes, resulting in coughing, wheezing, or other respiratory ailments.
10. Obesity/Lack of exercise
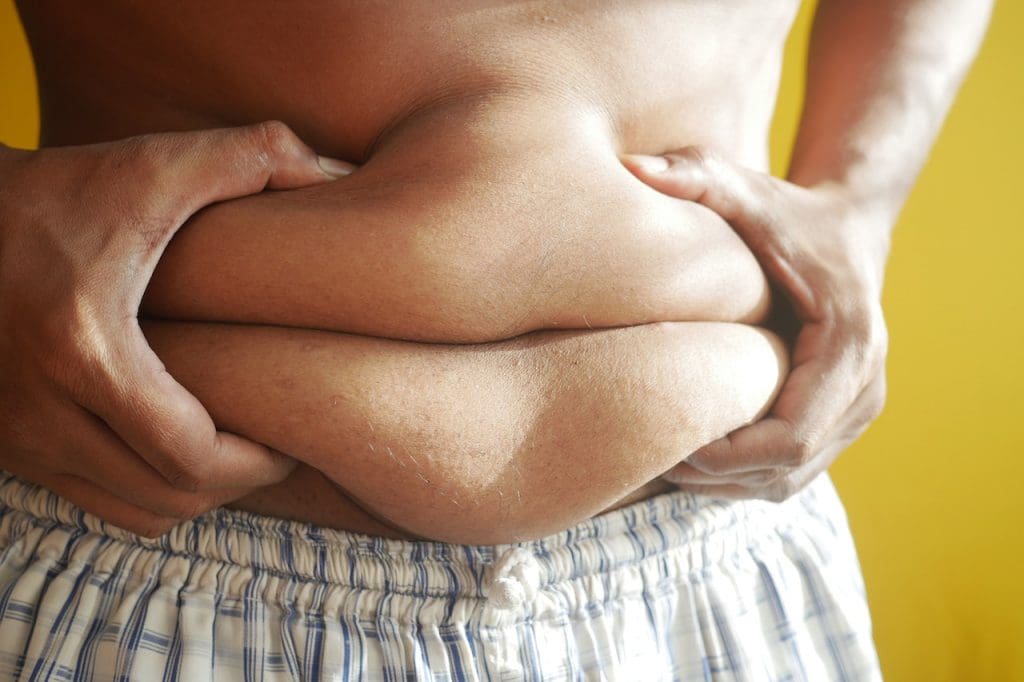

Being overweight increases your chances of having systemic problems due to extra fat tissues that put strain on organs throughout body and releasing large quantities of pro-inflammatory chemicals, called adipokines. Similarly, a lack exercise of contributes to a release of these same compounds, leading to greater risk of developing chronic illnesses, such diabetes or heart disease.
Conclusion
Reducing your overall level of chronic inflammation is key for maintaining good health over time by reducing your risk for many major illnesses associated with it. Eating a balanced diet full of unprocessed whole foods rich in antioxidants like fruits and vegetables has been proven beneficial for reducing overall levels of systemic inflammation. Additionally, regular physical activity helps maintain healthy levels by stimulating production of anti-inflammatory molecules within our bodies while eliminating stress hormones which cause heightened inflammatory responses over time. Reducing cigarette smoking, drinking alcohol only in moderation and avoiding sugary processed foods are all important steps towards lowering chronic systemic inflammatory markers within our bodies and promoting long term health.
Overall understanding what triggers your own personal inflammatory response is key to maintaining good health and protecting yourself from future diseases or illnesses. If you suspect you might be suffering from any type condition described here, you should seek medical advice as soon as possible to ensure that you receive the correct treatment promptly, and avoid any potential complications down the road.
